What is Distributed Architecture?
Distributed architecture refers to a network design approach that decentralizes key functions, moving them closer to the network edge. This method enhances efficiency, scalability, and performance by reducing reliance on centralized processing hubs.
How Distributed Architecture Works
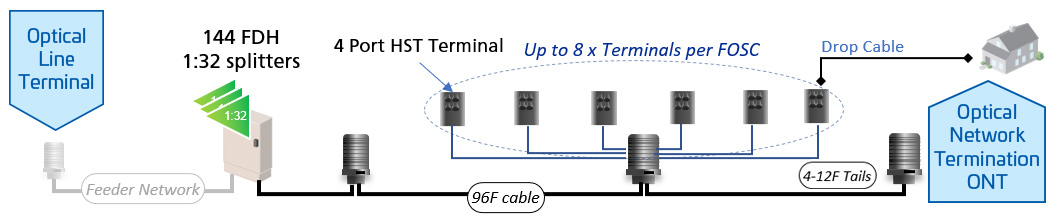
Rather than relying on a single centralized location, a distributed network spreads processing and data management across multiple nodes to enhance performance and resilience. This approach improves bandwidth utilization, reduces latency, and enhances overall network reliability.
Applications in Broadband Networks
Distributed architecture is widely used in broadband networks, particularly in Distributed Access Architecture (DAA) for cable systems. DAA shifts network functions from traditional headend locations to fiber-optic nodes, optimizing signal transmission and network efficiency.
Advantages of Distributed Architecture
This approach offers several benefits, including improved network scalability, enhanced fault tolerance, and better resource allocation. By distributing processing power, networks can adapt more effectively to growing data demands and evolving technologies.
Related CommScope Links: